UK foster care regulations have altered largely due to changes in societal perspectives, updated legislation, and increased emphasis on child safety and wellbeing. The shift towards a more vital-centered approach, improved adoption procedures, and increased financial support for foster parents are just a few factors that have influenced these changes. Importantly, these adjustments aim to provide a nurturing environment for foster children. Understanding the new regulations' implications, for foster parents, the children themselves, and all stakeholders involved is crucial. Continued exploration will provide a more thorough grasp of these evolving regulations.
Key Takeaways
- Foster care regulations in the UK have altered to improve the child-centered approach, emphasizing children's voices in decision-making processes.
- Changes aim to enhance foster parent training, equipping them with skills in trauma management and emotional support, thereby strengthening the foster care system.
- The government has introduced alterations in financial support for foster parents to address financial instability, balancing quality care provision with financial dependency.
- Regulatory alterations are necessary to address gaps in previous regulations, increase accountability, reflect evolving societal understanding, and enhance child protection.
- The shift in regulations is also influenced by a desire to streamline the adoption process, improve adoption rates, and adapt to technological advancements shaping the future of foster care.
Historical Overview of UK Foster Care
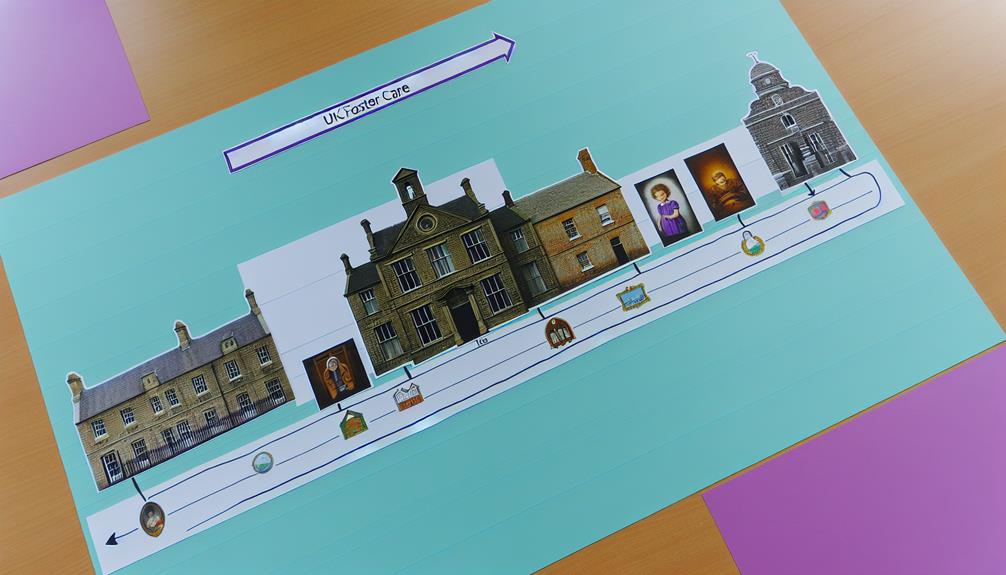

To fully appreciate the recent alterations in UK foster care regulations, it's crucial to explore the historical evolution of foster care in the UK. The origins of foster care can be traced back to the 19th century, intertwined with the development of child welfare services.
Historically, the Poor Law of 1834 was instrumental in shaping the early foster care system. It was designed to care for children whose parents were unable to do so, often due to poverty or illness. This was a pivotal first step in recognising the importance of providing support to vulnerable children.
Next came the Children Act of 1908, another milestone in the historical legislation of foster care. This Act set the groundwork for a more structured foster care system, introducing regulations for the treatment of children in care and the responsibilities of foster parents.
Then, the Children Act of 1989 revolutionised foster care, marking a shift towards child-centred care and recognising the rights of children in care. This Act had a profound impact on foster care, shaping it into the system we're familiar with today.
Key Changes in Foster Care Policies
In recent years, there's been a significant wave of changes in the UK's foster care policies, ushering in a new era of more detailed, child-centred regulations. This shift is driven by a need to better serve children's interests, but it hasn't been without policy criticism. Some argue these changes are too stringent or bureaucratic, potentially dissuading prospective foster parents.
A key alteration is the increased emphasis on the child's voice in decision-making processes. The child's wishes and feelings are now given due consideration when making decisions about placement and care planning. This progressive approach ensures that the child's welfare remains paramount.
Another major change concerns adoption rates. There's been a concerted effort to improve these, with new policies aiming to reduce delays in adoption processes. The government has introduced measures to streamline adoption procedures and expedite the placement of children into stable, loving homes.
Furthermore, foster care policies now mandate regular, all-encompassing reviews of each child's circumstances, ensuring their needs are continually met. These changes reflect a deliberate shift towards a more holistic, child-centred approach to foster care, underscoring the evolving nature of the UK's foster care system.
Impact of New Regulations on Foster Parents
As a foster parent, you'll notice significant alterations due to the new regulations. These changes aim to enhance your training, modify your rights, and adjust the financial support you receive.
You'll find it essential to understand these impacts to adapt effectively and continue providing the best care for your foster child.
Enhancing Foster Parent Training
With the recent changes to UK's foster care regulations, you'll notice a significant emphasis on improving the training provided to foster parents, primarily aimed at enhancing their skills and understanding of child care.
Innovative training modules are now deployed to foster resilience, enabling you to navigate the unique challenges of foster parenting. These modules focus on topics like trauma management, behavioural understanding, and emotional support, equipping you with the tools to create a supportive environment for your foster child.
They're also designed to be interactive and all-encompassing, ensuring you get a holistic understanding. As a result, the new regulations aim to strengthen foster care by empowering you with advanced knowledge and skills, ultimately contributing to the welfare of the children in your care.
Effects on Parental Rights
Beyond enhancing your training, the new foster care regulations also reshape your parental rights, effectively redefining your role and responsibilities as a foster parent.
These changes have triggered a shift in parental perspectives, as well as potential rights revocation in certain cases.
Here's a brief comparison:
| Old System | New System |
|---|---|
| Rights and responsibilities were fairly static | Foster parents' rights are now more dynamic |
| Parental perspectives were often overlooked | Parental perspectives are now considered in policy-making |
| Rights revocation was rare | Rights revocation is now more common, depending on circumstances |
These alterations may seem challenging, but they're designed to create a more inclusive, adaptable foster care system. Mastering these changes will enable you to provide excellent care for your foster child.
Changes in Financial Support
Under the new regulations, you'll notice significant changes in financial support for foster parents, altering the landscape of foster care economics. The shift aims to address financial instability often experienced by foster parents, ensuring support sustainability.
Yet, it's not without implications. The increase in financial aid might attract individuals to foster care for monetary gains rather than genuine care. Additionally, it could inadvertently foster a dependency culture, where individuals rely heavily on this support.
It's important to strike a balance; sufficient funds are necessary for providing quality care, but over-reliance could lead to issues. As a foster parent, it's essential to understand these changes, their implications, and adapt accordingly.
Foster care is about providing a loving home, not financial stability.
The Role of Government in Foster Care Changes

You must consider the significant role the government plays in shaping foster care changes. Their decisions and the rationale behind them cause ripple effects throughout the system.
From regulatory changes and their impacts, understanding the government's role is critical in maneuvering these changes.
Regulatory Changes Impact
Government involvement plays a crucial role in shaping the regulatory landscape of the UK's foster care system, fundamentally impacting the lives of numerous children in need. With increasing regulatory scrutiny, compliance challenges have emerged for foster care providers, prompting necessary adjustments and realignments.
These changes, while initially posing hurdles, aim to guarantee that child protection standards aren't just met but exceeded. It's about making sure every child in the foster care system is provided the best possible environment. These implications extend beyond the immediate foster care sphere, influencing social policies and strategies.
Governments Decision Rationale
Examining the rationale behind the government's decision, it's clear they're making these changes in the foster care system to prioritize the safety and wellbeing of children. The decision influences and policy motivations are rooted in the desire to reinforce a more robust, child-centered approach. The government's intent isn't to complicate the process, but to enhance the support and care that foster children receive.
This move also reflects the government's commitment to addressing societal concerns about child protection. The policy motivations are designed to guarantee children in foster care are provided with a nurturing environment. This is a strategic, yet compassionate approach by the government, prioritizing child safety and wellbeing, which is paramount in the foster care system.
How Changes Affect Fostered Children
Changes in UK foster care regulations have a significant impact on the daily lives of fostered children, shaping their experiences and potentially determining their future prospects. These alterations prominently affect the emotional landscape of these children. It's important to understand that changes in regulations can trigger a range of emotions, from relief and hope to anxiety and uncertainty.
On the brighter side, new regulations often aim at resilience building. For instance, modifications that encourage regular contact with birth families or promote stable, long-term placements can bolster children's confidence and coping abilities. However, sudden shifts in requirements can also create instability, potentially leading to emotional distress.
Furthermore, changes in foster care regulations can affect these children's social interactions. Revised rules may alter the circumstances under which they can engage with peers and participate in community activities, potentially impacting their social skills development.
Last, but not least, the educational prospects of fostered children may be influenced. For example, regulations that affect placement stability could disrupt schooling, while those that support continuity of education can enhance their academic achievements. Overall, the impact of these changes on fostered children is diverse and far-reaching, underscoring the need for careful consideration and thoughtful implementation.
Legal Implications for Foster Care Changes

While traversing the landscape of foster care changes, it's crucial to consider the legal implications that come with these alterations. Legal challenges may arise, such as guaranteeing new regulations align with existing laws, and the potential for disputes over policy interpretation.
As a stakeholder, you need to comprehend the legal framework that underpins these changes. Changes in foster care regulations can lead to modifications in the rights and responsibilities of foster parents, social workers, and the children themselves. This shift could potentially lead to legal disputes if not managed correctly.
Furthermore, policy interpretation introduces additional complexities. Each word in a policy can have significant legal implications. Hence, it's critical to ensure clarity in the language used, to avoid ambiguous interpretations that could lead to legal challenges.
Understanding the Need for Regulatory Alterations
To thoroughly understand these regulatory changes, it's essential to explore the underlying factors necessitating their implementation in the UK's foster care system. Regulatory motivations stem from a desire to enhance the quality of care and protection offered to children. This is achieved by improving policy effectiveness, ensuring policies are relevant, timely, and responsive to the changing needs of foster children.
One key motivation is the need to address gaps in previous regulations, which may have left children vulnerable or neglected. The alterations aim to increase accountability, ensuring that every child's rights and well-being are prioritised above all else.
Another factor driving these changes is the evolving societal understanding of children's rights and needs. Over time, it's become clear that the old regulations didn't fully meet these needs, leading to the implementation of more holistic and child-centric policies.
The effectiveness of these new policies is measured not only by compliance rates but also by the improved quality of life for foster children. Hence, the need for regulatory alterations arises from a commitment to uphold the rights of children, to adapt to societal changes, and to continually improve the foster care system.
Future Projections for UK Foster Care

Looking forward, it's crucial that these regulatory amendments to the UK foster care system carry implications for the future landscape of child welfare and protection. You'll likely see shifts in adoption trends as a result. The changes aim to streamline the process for potential foster parents, potentially leading to an increase in successful adoptions.
Technological advancements will also play a significant role in shaping the future of UK foster care. Digital tools could facilitate matching processes between children and potential families, increasing efficiency and reducing wait times. Additionally, technology might enhance ongoing support and training for foster parents, improving their ability to provide quality care.
However, it's important to remember that these projections aren't set in stone. They hinge on the successful implementation of regulation changes and how well the system adapts to technological advancements. The future of UK foster care is intricately tied to the effectiveness of these alterations, fostering an environment that prioritises child welfare and protection.
Therefore, as you watch this space, consider these projections as possibilities, not inevitabilities. The ultimate goal remains – to provide the safest, most nurturing environment for every child in need of care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Process to Become a Foster Parent in the Uk?
You'll need to meet eligibility criteria, such as being over 21 and having a spare room. Then, you'll undergo an assessment process involving checks, interviews, and training to become a foster parent in the UK.
How Are Foster Parents Trained and Supported in the Uk?
Ever wondered how you'd be prepared as a UK foster parent? Through rigorous training evaluations and robust support networks, you're equipped with necessary skills and emotional resilience to provide a safe environment for your foster child.
What Financial Support Is Available for Foster Parents?
As a foster parent in the UK, you're granted access to various funding sources like weekly fostering allowances. Additionally, you'll enjoy tax benefits that substantially reduce your taxable income, easing your financial burden.
How Are the Rights of Biological Parents Affected by These Changes in Regulations?
As the saying goes, 'No man is an island.' Parental challenges can arise with changes in foster care regulations, impacting your rights as a biological parent. It's important to understand these impacts thoroughly.
Are There Specific Regulations Regarding the Fostering of Children From Diverse Ethnic and Cultural Backgrounds?
Yes, UK regulations emphasize cultural sensitivity training for foster parents. However, the ethnic matching controversy questions if it's more essential to place children quickly or wait for ethnically identical foster homes.
Conclusion
So, you see, the landscape of UK foster care has undergone seismic shifts, not unlike a kaleidoscope, constantly changing patterns.
These transformations, driven by government initiatives, have notably impacted both foster parents and children. They've introduced legal complexities, but they're essential to guarantee the welfare of fostered children.
Looking ahead, we anticipate a future of continuous evolution in foster care regulations, adapting to the changing needs of society.